Are you new to EVE-NG? Don’t worry! This tutorial is designed for beginners and aims to guide you through installing and configuring EVE-NG on your computer. Whether you have prior experience, this tutorial will provide the essential steps to ensure a successful installation and setup.
We’ll be with you every step of the way, providing clear instructions to help you successfully install EVE-NG. From installing VMware Player to creating your first lab, we’ll ensure you have everything you need. We’ll even guide you through configuring your first EVE-NG lab.
So don’t worry; by the end of this tutorial, you’ll feel confident and accomplished in setting up your EVE-Ng environment. Ready? Let’s go!
(NOTE: The Ultimate Free EVE-NG Course – Master network simulation with our step-by-step guide and elevate your skills from beginner to pro. Start your free course now!)
Table of contents
- What is EVE-NG?
- Getting Started with EVE-NG
- Before You Begin, Here’s What You Need
- Step 1. VMware Workstation Player Installation
- Step 2. How to Download and Install EVE-NG
- Step 3. Creating Your First Lab in EVE-NG
- Step 4. How to Start Building Your First EVE-NG Lab
- Step 5. How to Configure Static Routing on a Cisco Router
- Wrapping Up Your EVE-NG Journey
- Where to Go From Here
What is EVE-NG?
EVE-NG is a popular network emulation software that allows individuals and organizations to design, configure, and test various network scenarios. It’s designed for both educational purposes and real-world network testing and development. EVE-NG provides a flexible and scalable environment for emulating complex network topologies, including routers, switches, firewalls, and more, all within a virtualized environment. There are three versions of EVE-NG licenses. The community version is free, the pro version is paid, and the learning center is ideal for IT learning centers or universities.
Getting Started with EVE-NG
You might be wondering, Which version of EVE-NG should I install? Great question! If you’re unsure which version of EVE-NG to install, don’t worry—I’ll help! We’ll go through each version step by step to ensure you choose the right one for your needs. Let’s examine each version of EVE-NG and see what sets them apart.
Exploring the Three Versions of EVE-NG Licenses
EVE-NG offers three main licensing options: the Free Community Edition, the Paid Pro Version, and the Ideal Learning Center Option.
- EVE-NG Community: The Free Community Edition of EVE-NG allows users to explore and experiment with the software without financial commitment. This version provides basic functionalities and features that allow users to set up and manage virtual networks. While it may have limitations, such as restricted access to some advanced features or restricted usage of commercial images, the Free Community Version is still a valuable resource for network enthusiasts, students, or professionals on a budget.
- EVE-NG Professional or Pro: On the other hand, the Paid Pro Version of EVE-NG offers an enhanced experience with additional features and advanced functionalities. By subscribing to the Pro Version, users can access a wider range of network appliances and images, allowing for more comprehensive network simulations. This license also provides priority support from the EVE-NG team, ensuring prompt assistance whenever needed. The Paid Pro Version caters to individuals and organizations requiring a more extensive network environment for testing, research, or training purposes and is willing to invest in a premium experience.
- EVE-NG Learning Center: Lastly, the Ideal Learning Center Option is explicitly designed for educational institutions or training centers that aim to incorporate EVE-NG into their networking curriculum. This option provides extensive benefits for instructors and students alike. It offers seamless integration with learning management systems (LMS), simplifying virtual labs’ setup and management for large-scale deployments. Furthermore, the Ideal Learning Center Option includes dedicated technical support and ongoing updates to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted learning experience. Educational institutions can optimize their network training programs and empower their students with practical, hands-on experience by choosing this option.
In conclusion, EVE-NG offers a range of licensing options tailored to different needs and requirements. A suitable EVE-NG license is available whether you are an individual looking to learn and experiment with network configurations, a professional needing advanced functionalities, or an educational institution or training center seeking an ideal networking education platform. So, explore the licensing options to find the perfect fit for your networking endeavors.
Before You Begin, Here’s What You Need
Before installing your EVE-NG, you’ll need a few essential things. Let’s break down each of these so you know exactly what to look for and how to get started.
Minimum System Requirements
Knowing the minimum system requirements is essential to ensure a smooth installation process. According to the EVE-NG team, you will need at least a 64-bit operating system, 8GB of RAM,10 GB of free space, and a quad-core CPU. An SSD is also recommended for better performance. Meeting these requirements allows you to enjoy a seamless experience while exploring various networking scenarios on EVE-NG.
VMware Workstation Player
VMware Workstation Player is a handy program that offers a great solution for running a virtual computer on your own physical computer. It’s completely free and serves as a necessary tool for installing EVE-NG. To get it, click the link below and download the free version of VMware Workstation Player.
→ Get your free copy of VMware Workstation
EVE-NG Community Edition
In this tutorial, we will use the free EVE-NG Community Edition. This makes it a perfect choice for beginners seeking hands-on experience or individuals who want to practice specifically for the Cisco exam. Later in the tutorial, we will cover the installation process of EVE-NG.
WinSCP
For Windows Secure Copy, WinSCP is a file management software designed for the Windows operating system. It provides a secure and reliable way to transfer files through SSH (Secure Shell) and SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol). If we want to use image files in eve-ng, we must upload and install them. We need images to upload the file.
→ Get your free copy of WinSCP
EVE-NG Windows Client Side
The EVE-NG Windows Client Side is a handy tool that enables us to connect conveniently to network nodes within EVE-NG labs. Using the EVE-NG Client pack, we can seamlessly interact with network nodes and carry out various tasks. This tool supports telnet/ssh and vnc protocols, which provide secure and efficient connectivity options.
vIOS Router Image (I will provide you the download link )
IOSv is a virtual version of Cisco IOS that operates as a complete virtual machine on a hypervisor. This allows users to simulate the functionality and features of Cisco IOS without having to install it on hardware physically, and running it as a virtual machine offers network administrators and professionals greater flexibility, scalability, and convenience. It is a valuable tool for testing, learning, and experimentation in a virtual environment.
Step 1. VMware Workstation Player Installation
For EVE-NG installation, the easiest way is to install it over VMware Player or Workstation. As VMware Player is the free version and there is no need to pay for a license, we will install EVE-NG over VMware Player, making it easy for you to elaborate on the installation.
Tip — To download VMware Player, download the setup file. → Get your free copy of VMware Workstation
1. Once you download the Setup file, you should see the downloaded file like the below screenshot.
2. Then it would be best if you double-click on the VMware Player Setup file to install it on you’re PC.

3. Once the wizard is ready for installation, click on → Next to initiate the installation.
4. We need to accept the license agreements.
5. In this stage, we can select the Enhance Keyword Driver option or leave it unchecked.
Click on → Next.
6. Next, you must decide whether to get a new product update or join the VMware Customers Experience Improvement Program, which we are leaving to the default and will click → Next.
7. We can create an icon on the Desktop or Start Menu and click → Next.
8. Now is the time to install a VMware workstation on your Windows PC. Click → Install.
9. Please Wait!…
10. Great, the VMware Workstation Player is ready. To install EVE-NG in our system, Click on and click → Finish.
11. The VMware Player icon is on the desktop. It would be best to double-click on it.
12. We have two choices. We can select the free, non-commercial version by clicking the option below and then Clicking on it and clicking → Continue.
13. Lastly, click on →Finish.
14. Now, the VMware Workstation Player is ready for you.
Step 2. How to Download and Install EVE-NG
Now is the time to download the latest EVE-NG OVA file. Don’t worry if you’re looking for the EVE-NG OVA file; we’ve covered you. You can directly download it by visiting this link. Additionally, if you prefer to download the iso file, you can visit the EVE-NG website and obtain it through the provided link.
Note — The OVA version of EVE-NG has been removed from their website, and only the ISO version is currently available. We recognize that using the OVA is the simplest method for installation on a virtualizer. Therefore, we have produced an OVA version from the ISO for your convenience. To access the download link, please Download EVE-NG community OVA.
(NOTE: The Ultimate Free EVE-NG Course – Master network simulation with our step-by-step guide and elevate your skills from beginner to pro. Start your free course now!)
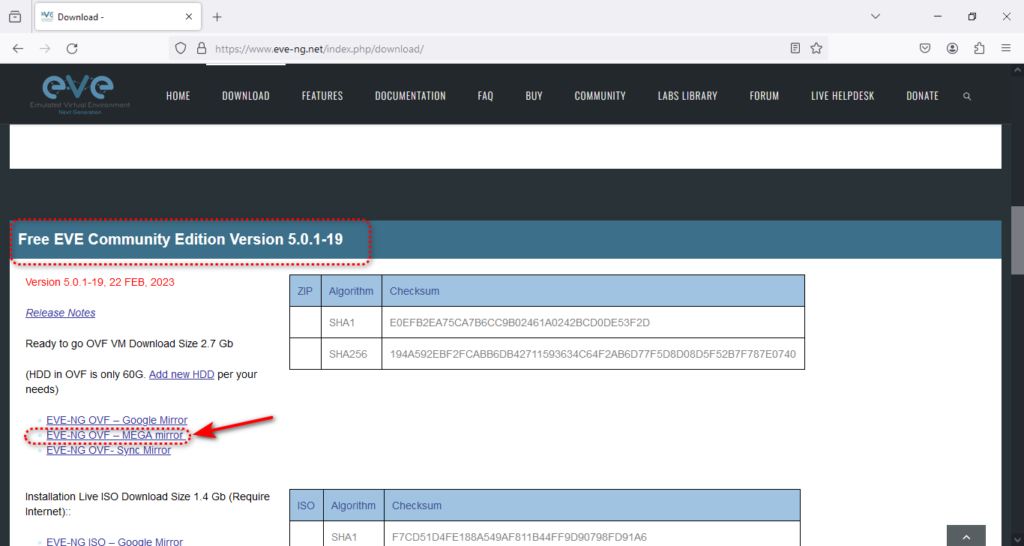
Now is the time to download the eve-ng ovf the file, like the screenshot below.
Then, you should see the downloaded file like this.
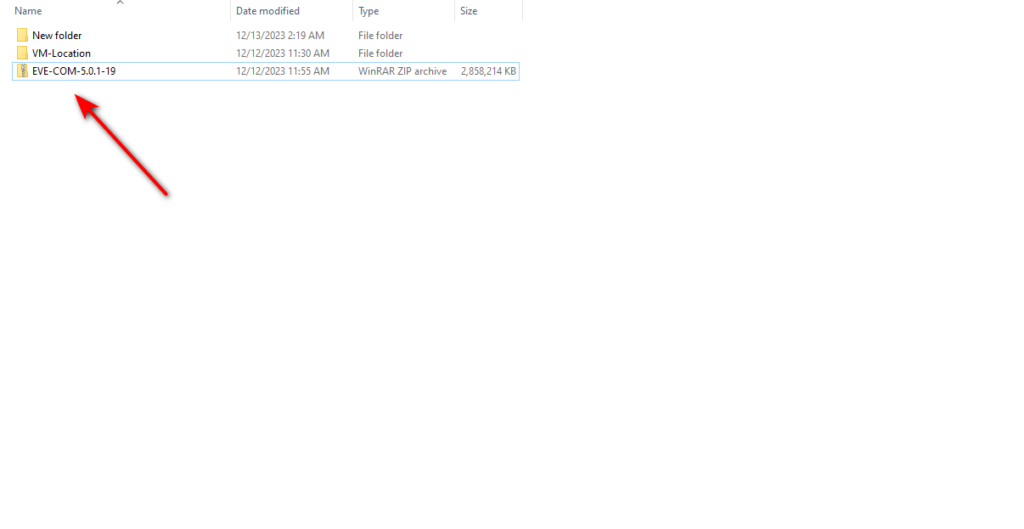
The downloaded file is a zip file. You must extract it to get the off format and install it on your VMware Player. To do that, right-click on the downloaded file and select the “Extract All” option.
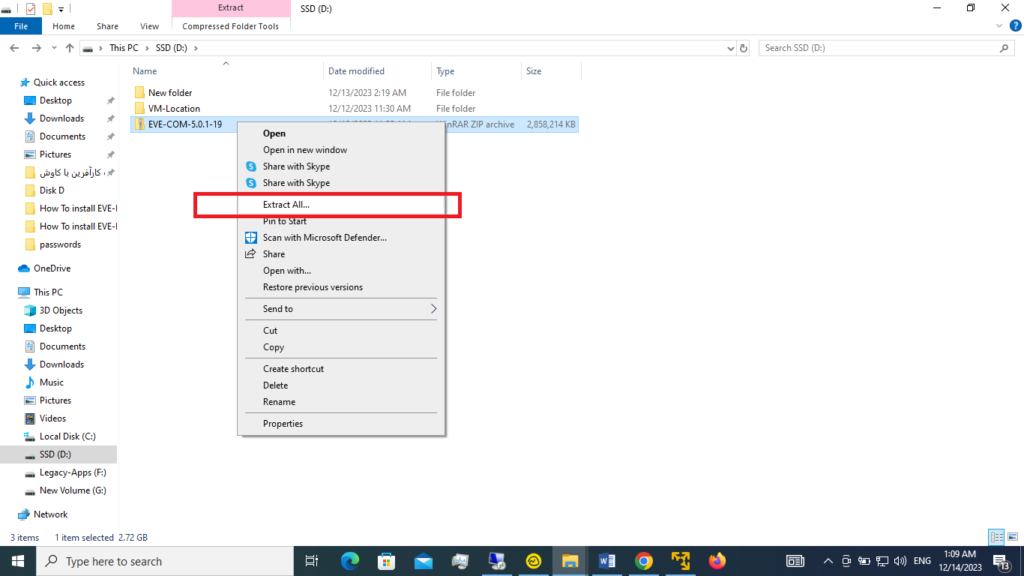
Then, you need to click on the extract option.
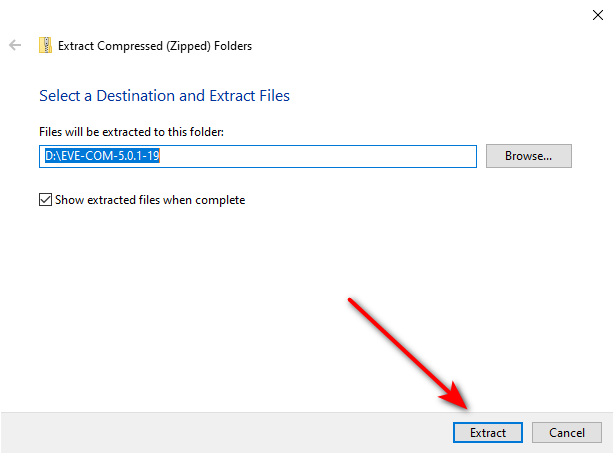
Now you need to go to the extracted folder to see the Ovf format of eve-ng.
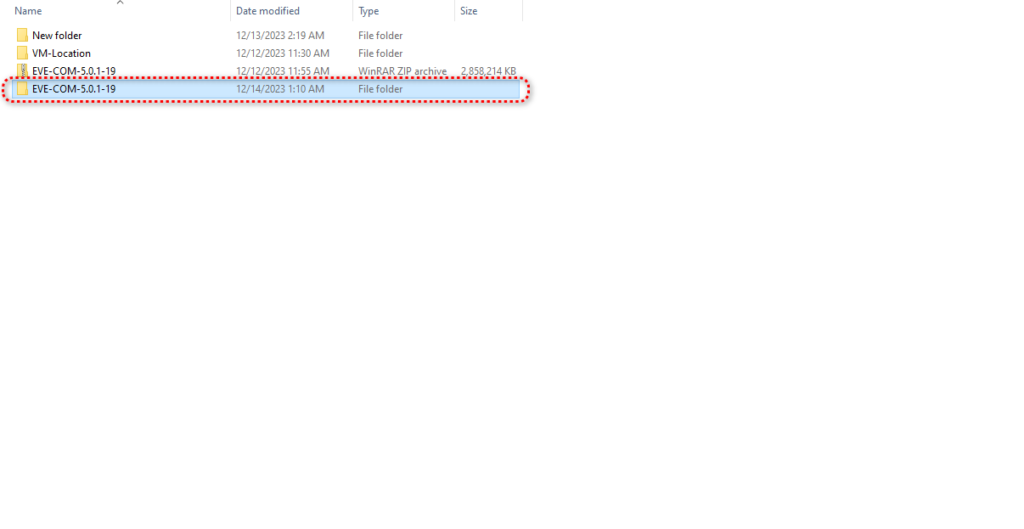
In the extracted folder, you can see the off file. At this stage, you need to double-click on the file and install the eve-ng of the file in Vmware Player.
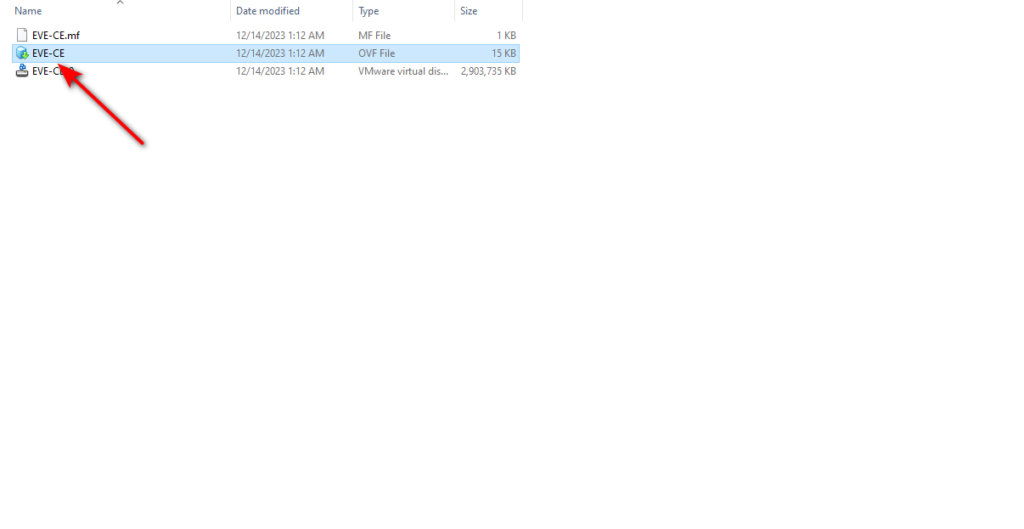
Then, you need to give the VM a name, specify its storage path, and click on import.
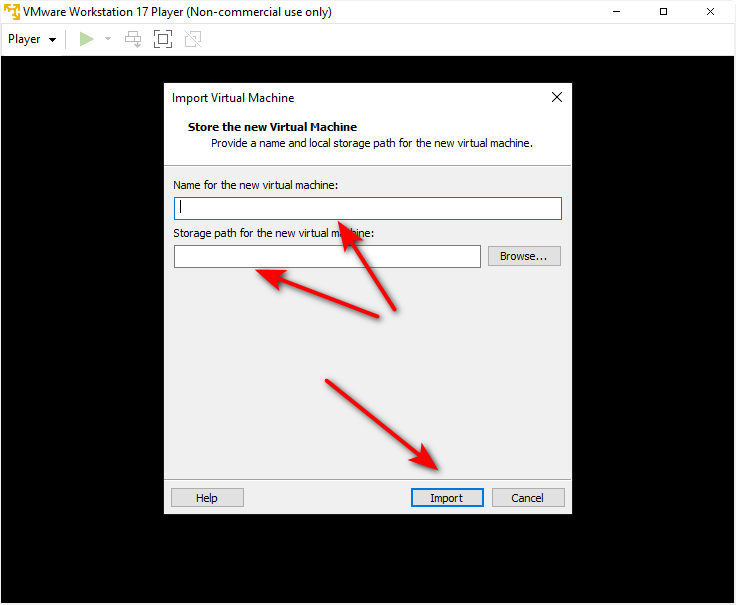
Like the screenshot below.
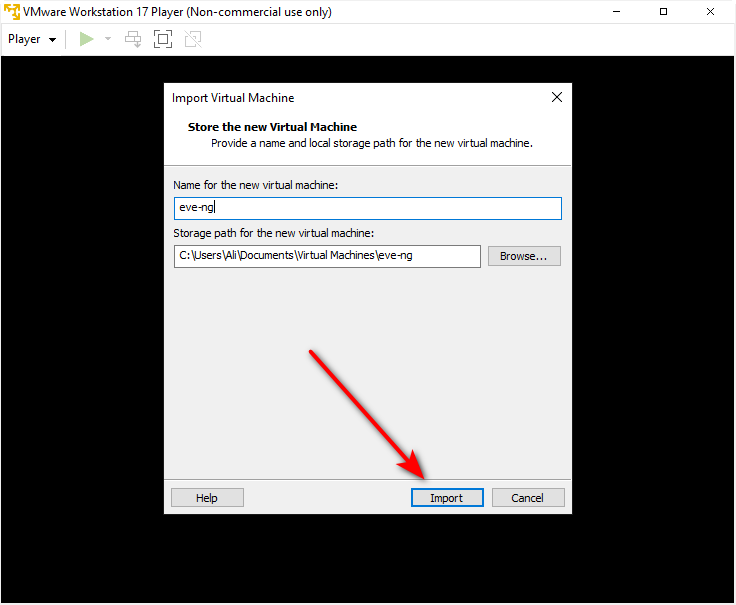
You can see the installation process at this stage, which might take 5 to 10 minutes.
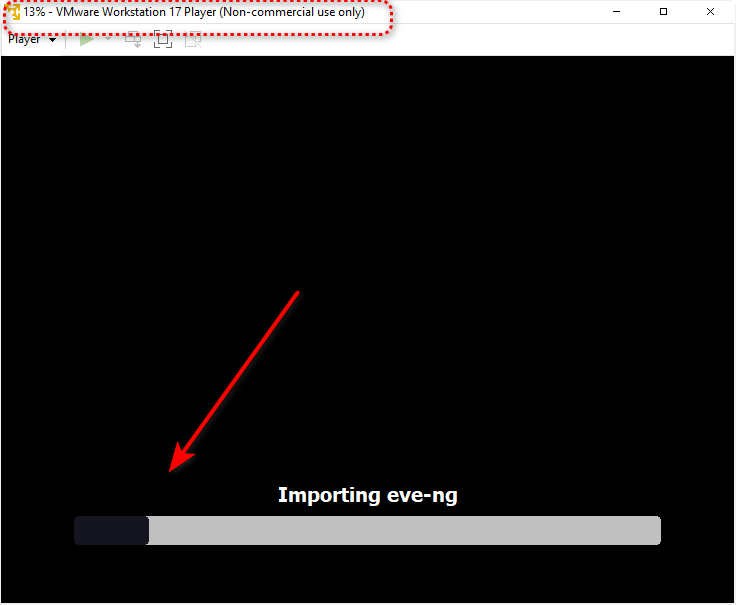
When the installation is finished, the eve-ng VM will start booting automatically. It would be best to wait to see if the installation is completed, and you should see the eve-ng VM IP.
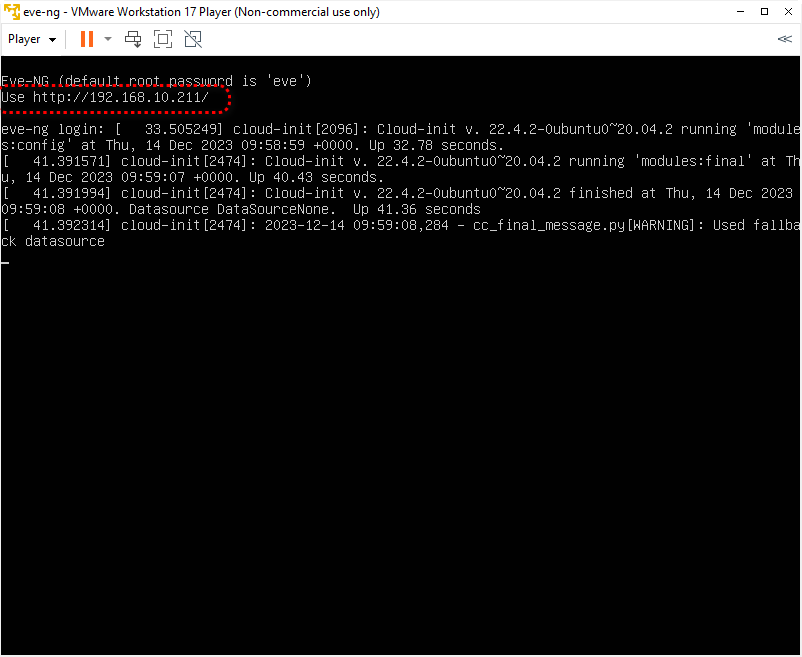
Now is the time to connect to the EVE-NG web console. The default credentials for the web are admin/eve, and for cli, they are root/eve. And make sure you have selected the native console option.
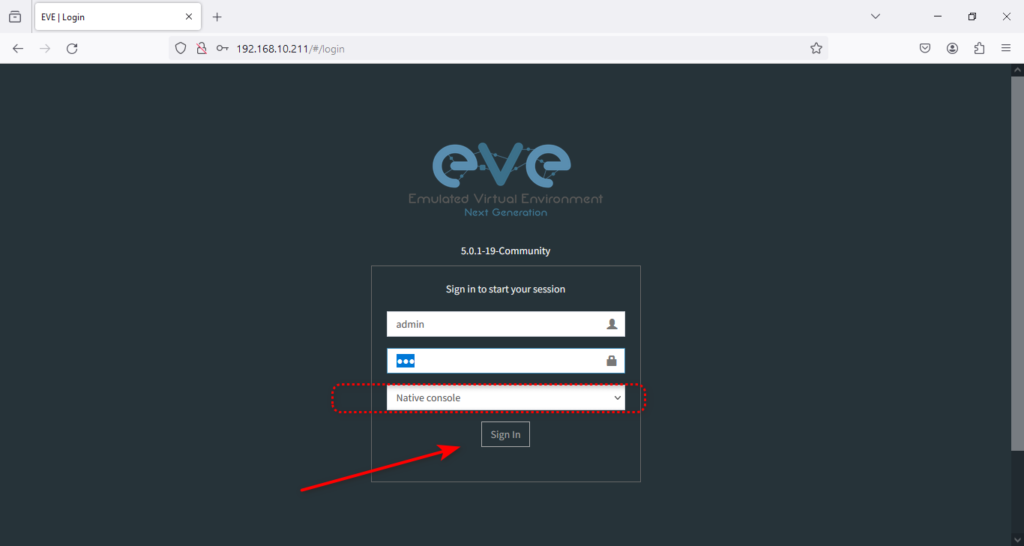
Congratulations, you have successfully installed EVE-NG on VMware Player.
Step 3. Creating Your First Lab in EVE-NG
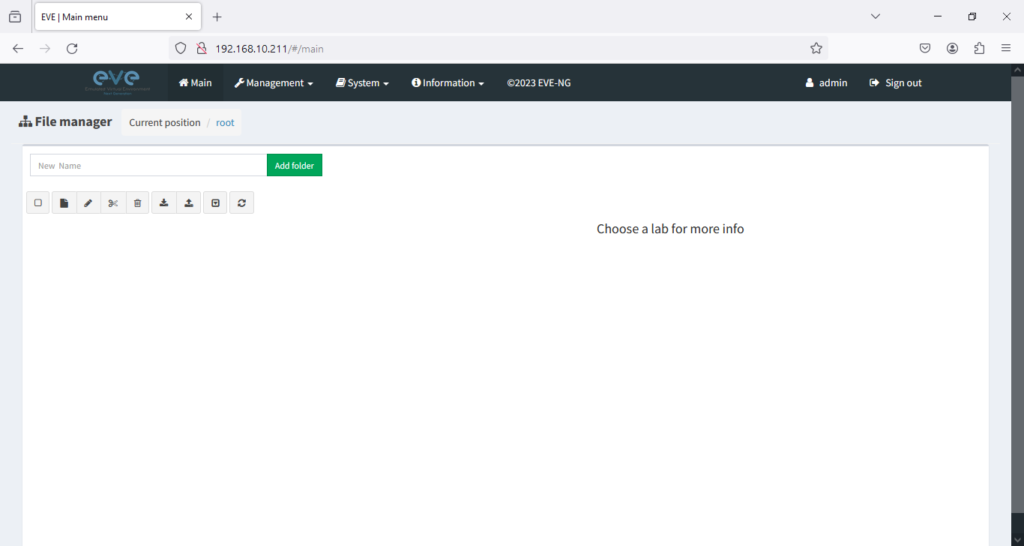
Creating your first lab in EVE-NG is quite simple. To begin, open the EVE-NG web interface and login to your account.
After logging in, you will be greeted by a screen that resembles the image below.
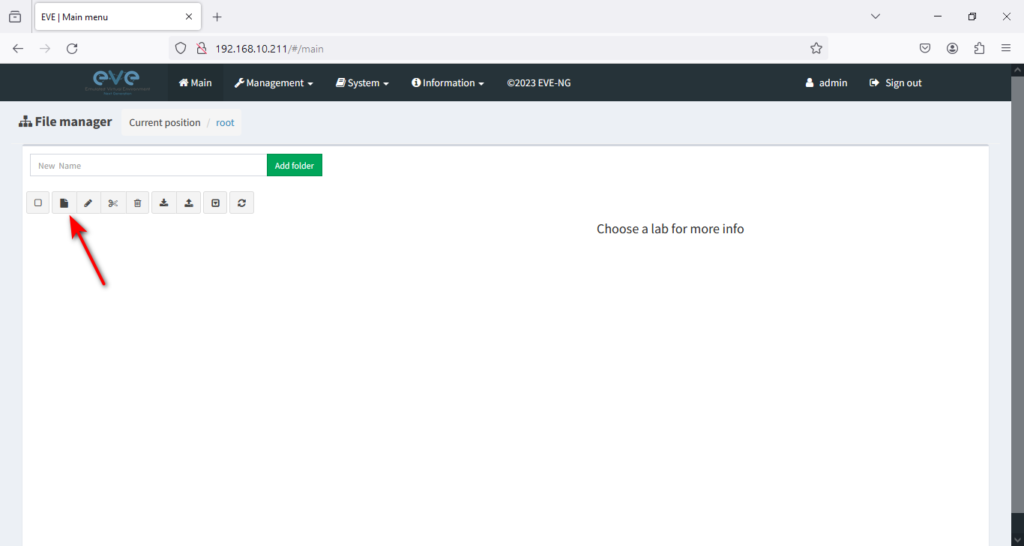
Next, click on the New Lab icon to create a new lab.
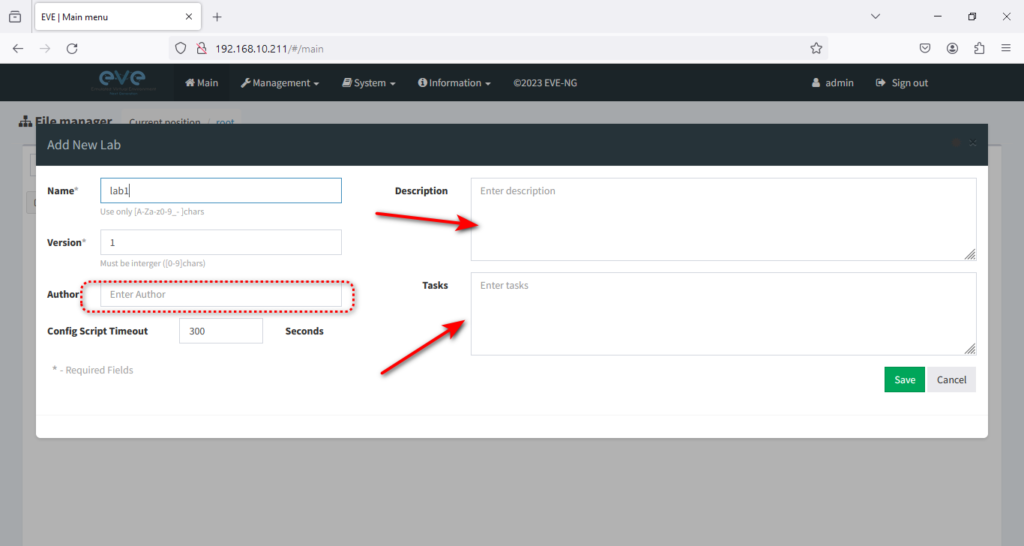
This will open a window. You need to give the lab a name, author, description, and task and click on → Save.
Once you have saved the new lab information, a redirect will take you to a new page. This page will allow you to begin crafting your desired scenario.
To begin, you only have to click on the + icon. This will allow you to add a node and start with whatever task you have. It’s a straightforward process that doesn’t require much explanation. So, click on that + icon to begin your journey!
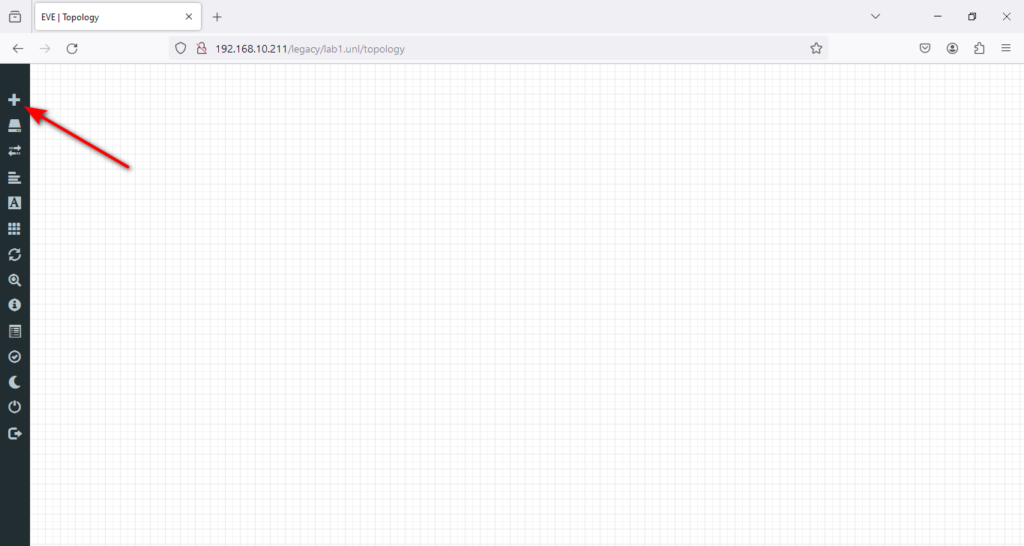
Or right-click on the lab and select Node.
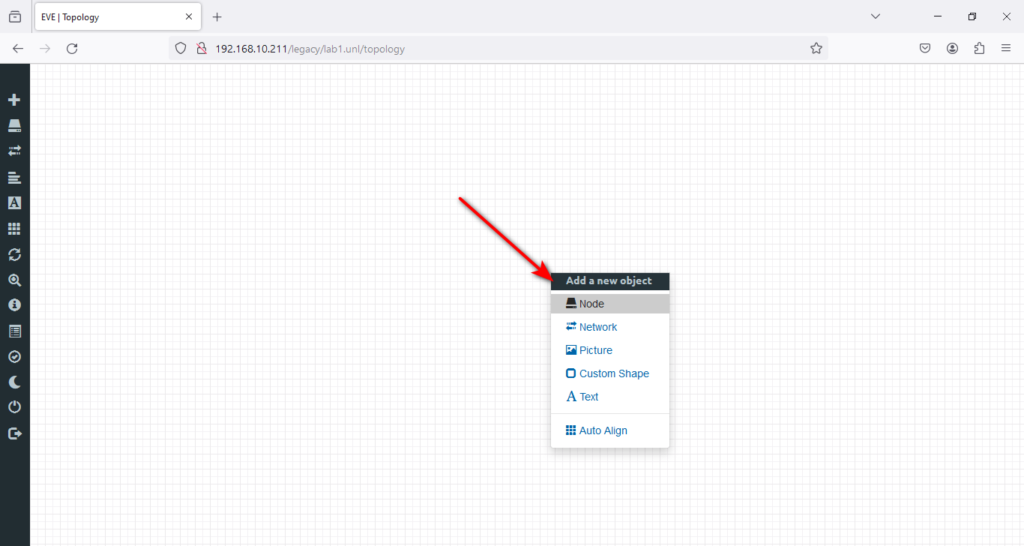
As you can see, no image is installed, and you need to install a new image to start your first lab. The only image available is the VPCs node, which is great for a client node. I will install the Cisco IOSv Router as it’s a standard router that we can use to start creating a lab and practice static routing in the lab.
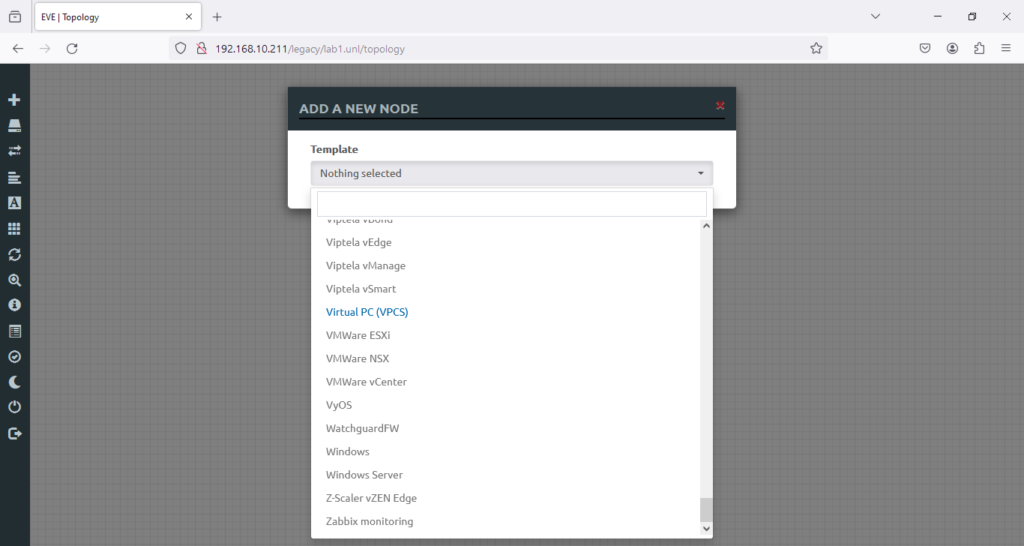
I’m going to install this version of vIOS router vios-adventerprisek9-m.spa.158-3.m2 (which you might have downloaded it from the above link)
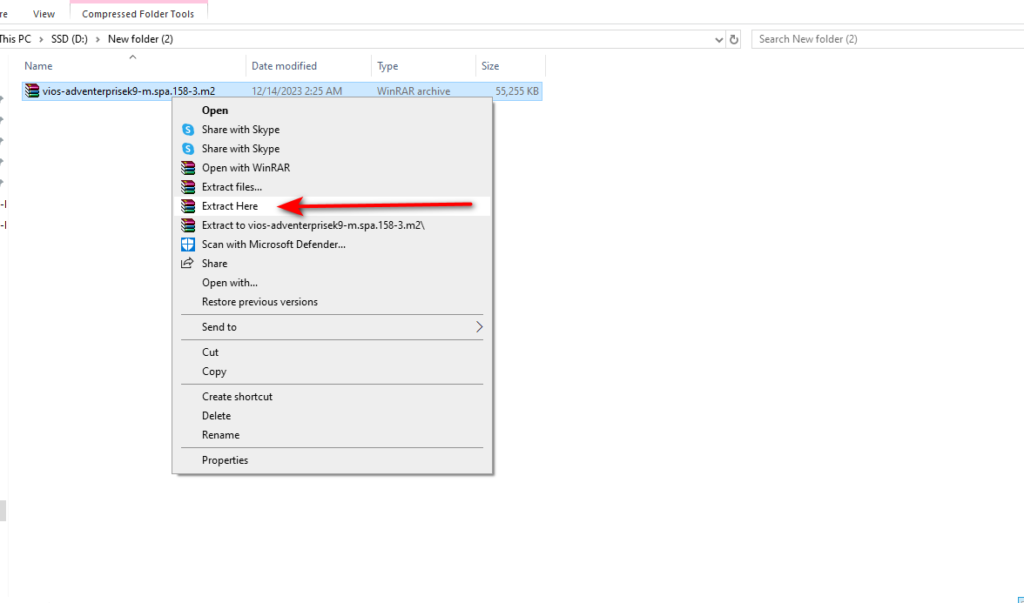
Note that the image format is in qcow2 format and compressed in zip format; you must unzip it first. Like the screenshot below, choose → Extract here or → Extract all.
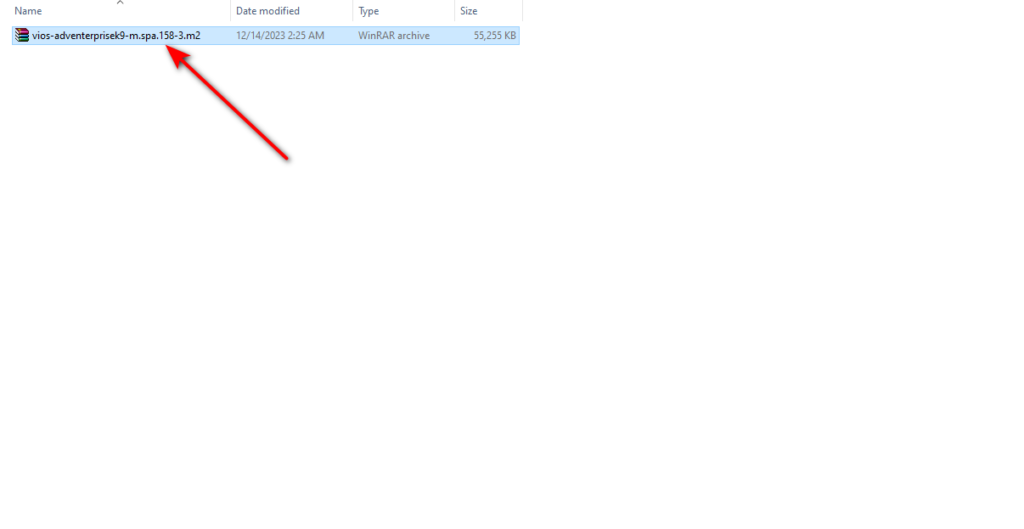
Right-click the image and select the Extract Here option in WinRAR or 7zip.
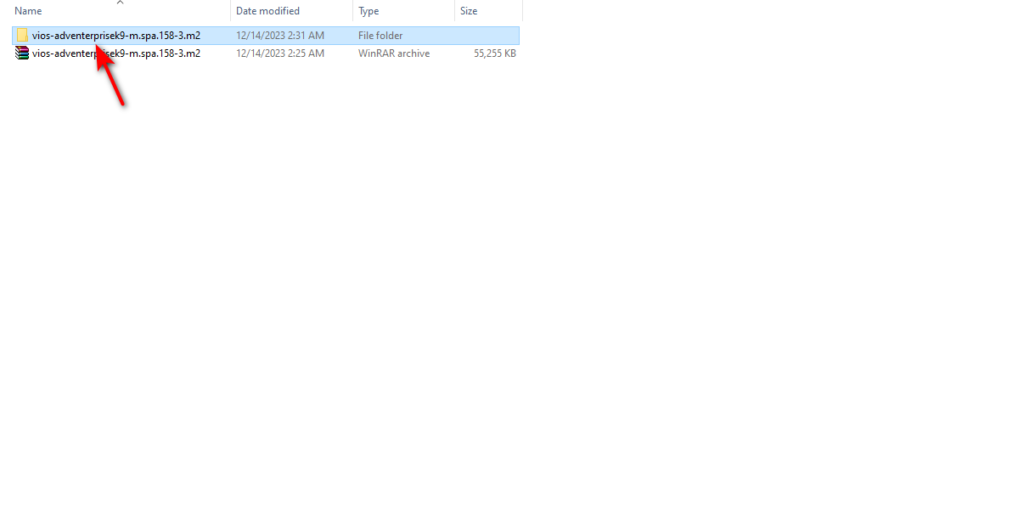
After extraction, you will see the image folder name and qemu image name, which we have prepared for you. You only need to upload it to your eve-ng.
Tip — Please do not change the folder and image file name.
We need to download WinSCP or FileZilla to upload this image to the desired directory on our EVE-NG.
Here is the directory path: →/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu
To upload the necessary image in EVE-NG, you must install WinSCP. If you are unsure how to install WinSCP, refer to the video tutorial below. It will guide you through the process with easy-to-follow instructions.
If you’d like to try WinScp, you can easily download it by visiting its official website at WinScp. Alternatively, you can also download it from the right → Get WinScp.
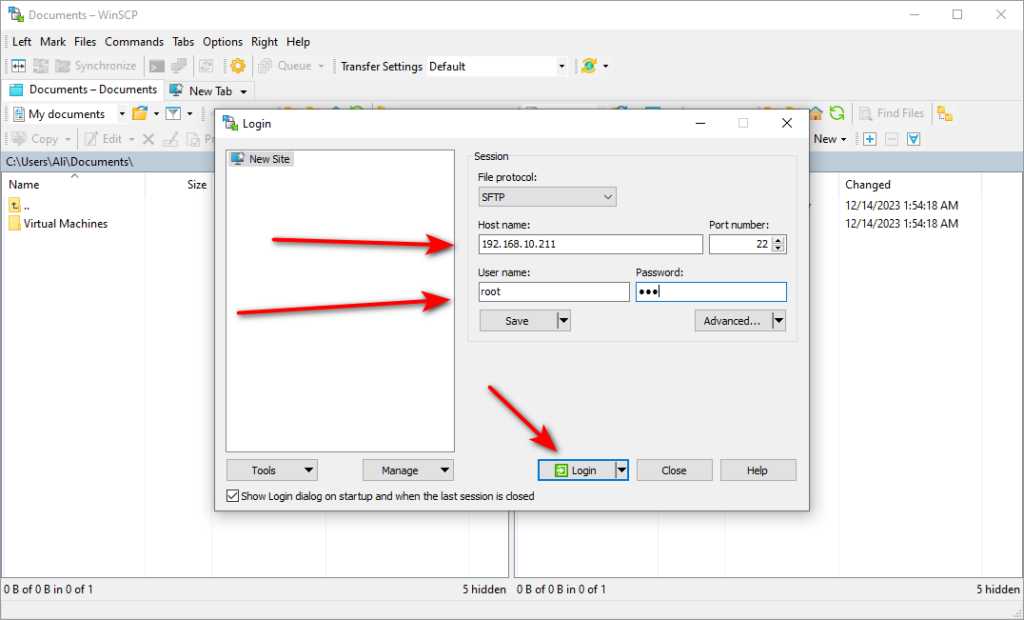
Now, we need to connect to EVE-NG with Winscp.
We need the EVE-NG IP and CLI username, which is the root. The password is eve, and the port is 22. Then, we will hit log in.
Tip—If you recall from the screenshot below, you can find your EVE-NG IP address and connect to it with Winscp.

Now is the time to connect to EVE-NG VM with IP and credential, which is default {root/eve}
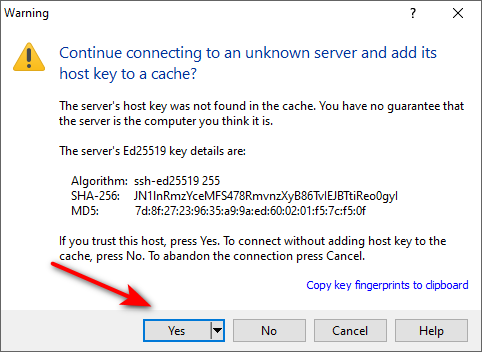
At first login, we need to accept the warning below.
As shown in the screenshot below, the red area is your EVE-NG server, and the blue area is your PC. We need to upload the image from your computer to this EVE-NG directory.
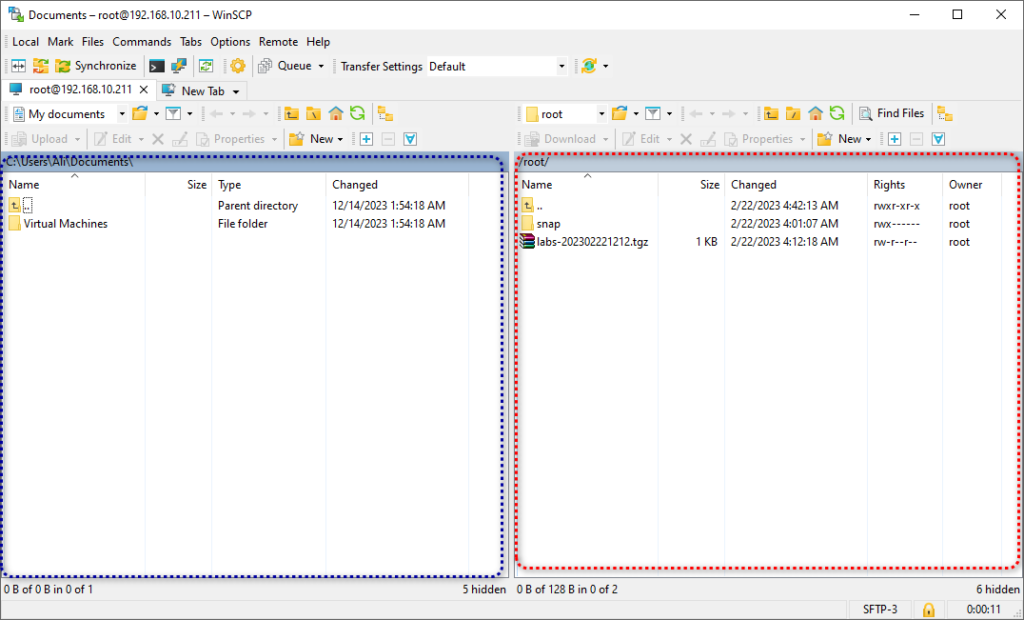
To upload the image from your computer to the EVE-NG directory, refer to the video below. It will guide you through the process step by step.
After successfully uploading the vIOS router, we can return to the eve-ng dashboard and continue with our work.
Will click on the router and accept the default settings.
Finish.
Step 4. How to Start Building Your First EVE-NG Lab
Now is the time to build an EVE-NG lab for static routing, one of the crucial majors in Cisco technology. We need to add two more Vios routers to connect them and start practicing static routing. The scenario should be like this (I will upload the lab .unl file, too, where you can easily import it and you don’t need to create this lab from scratch)
To create this scenario, we need to give each router a name. Which are R1, R2, and R3.
1. To do that, right-click the first router and select the Edit option.
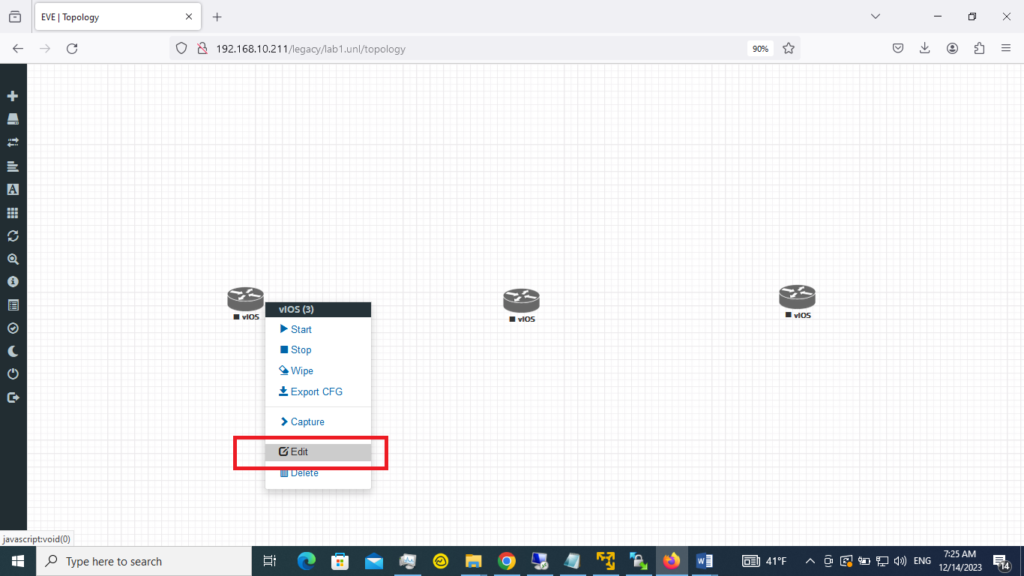
2. Then, I will type a name in Name/prefix, R1.
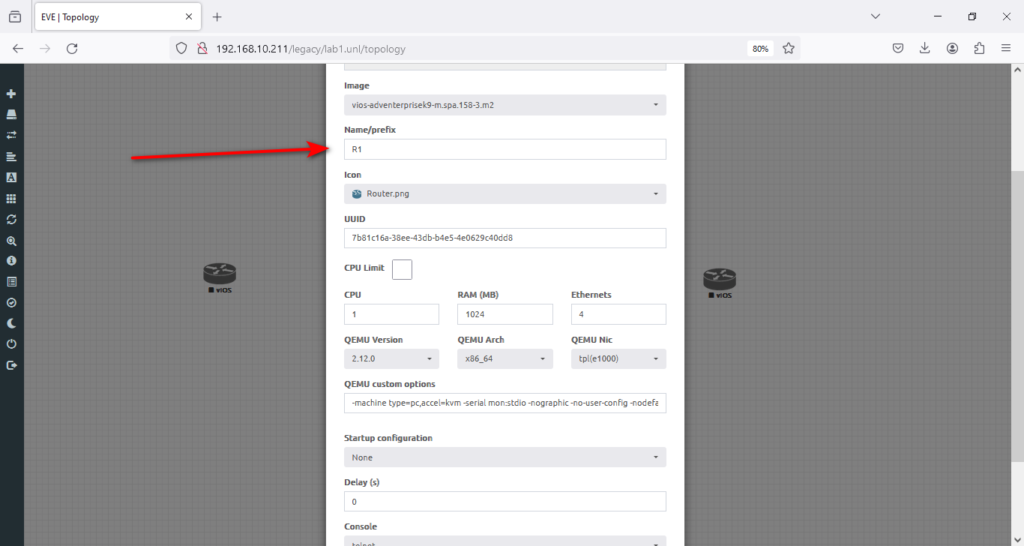
3. Then, I will hit save. Now, assign all images a desired name, R2 and R3. Once finished, you must see R1, R2, and R3 in the lab. You should see the plug button by hovering the cursor over the router. What we need here is to connect the routers.
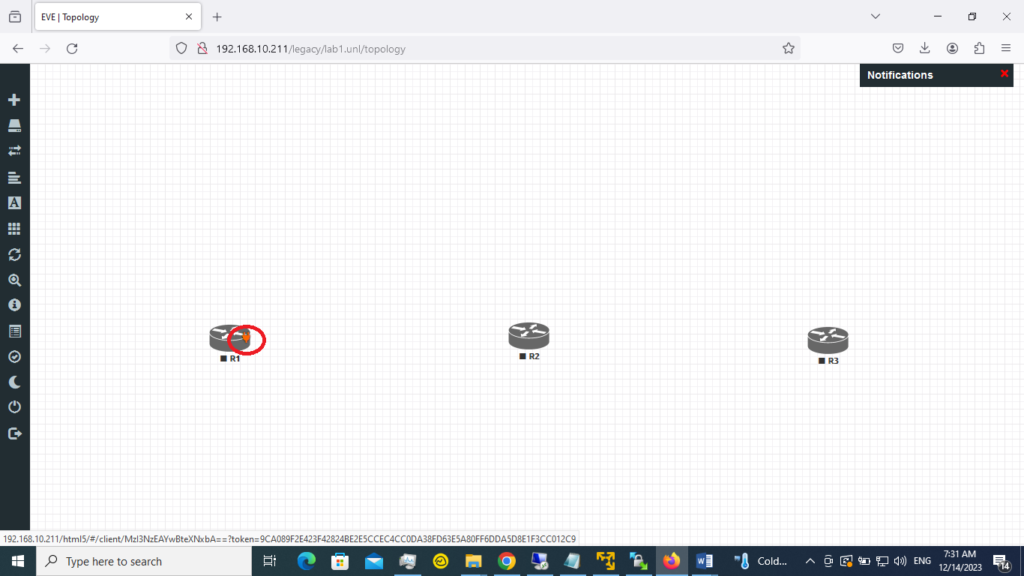
4. Select R1 and connect it to R2; drag the mouse from R1 to R2 by choosing the plug button.
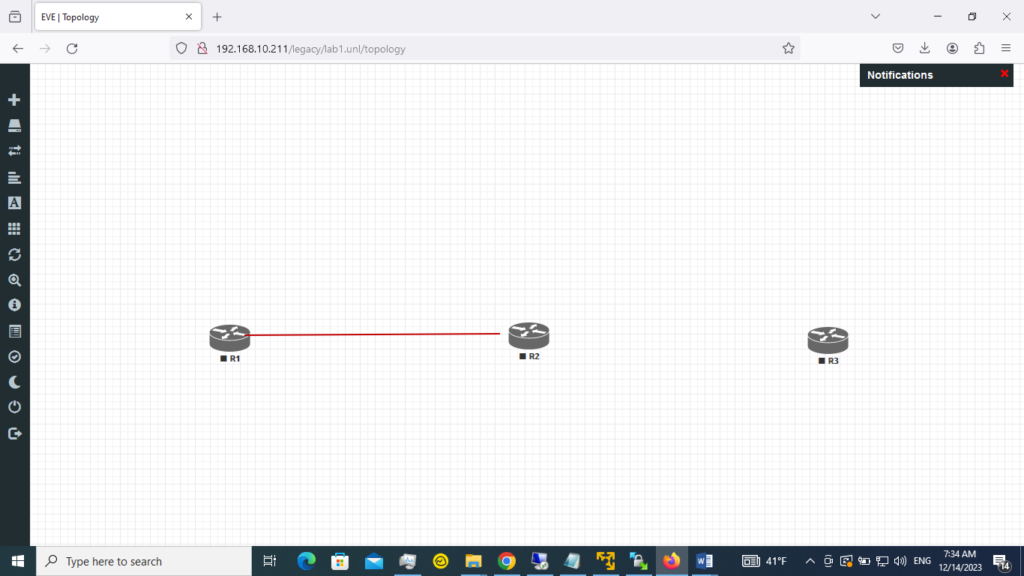
5. Here, we will accept the default connections for both routers in the G0/0 interface.
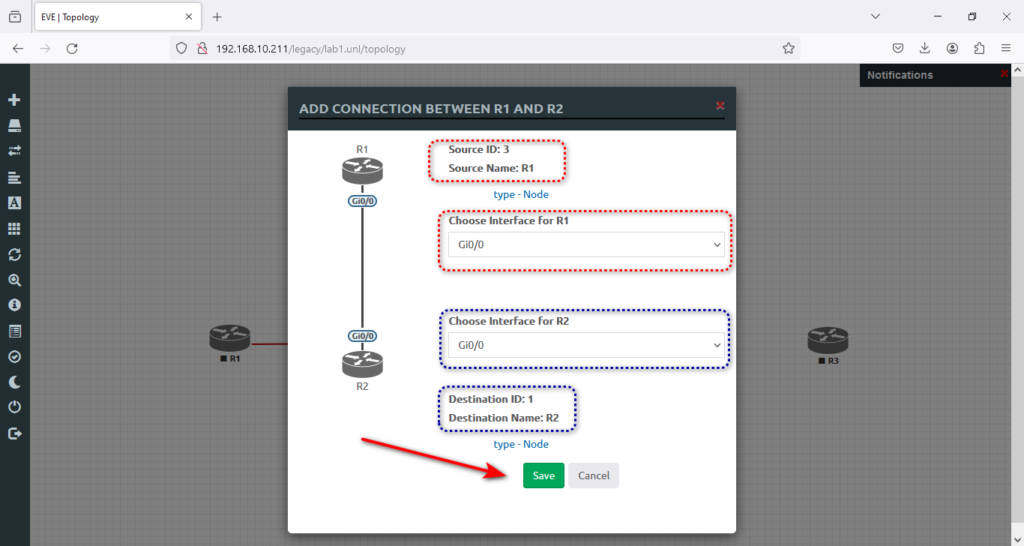
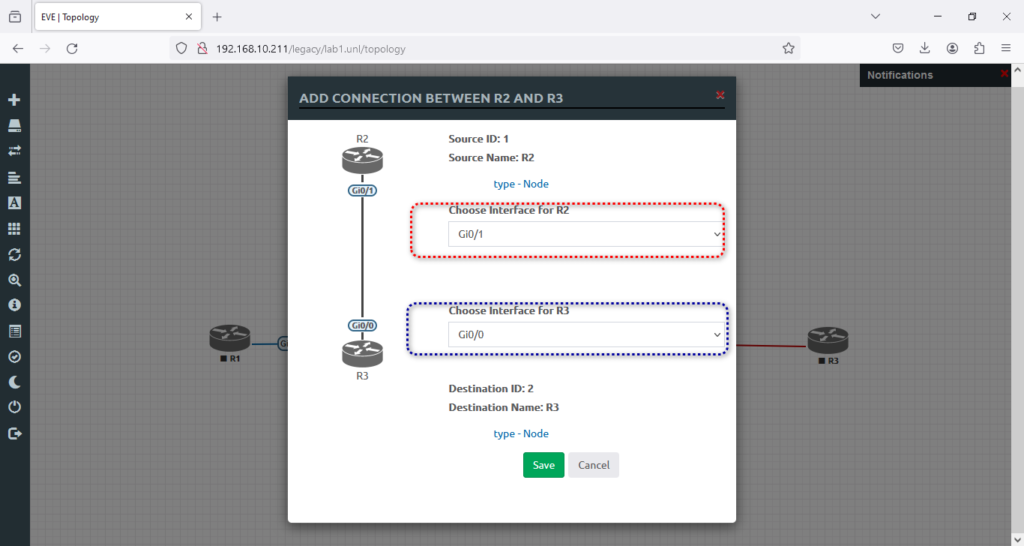
6. And now is the time to connect R2 to R3, like the screenshot below, and will hit → Save.
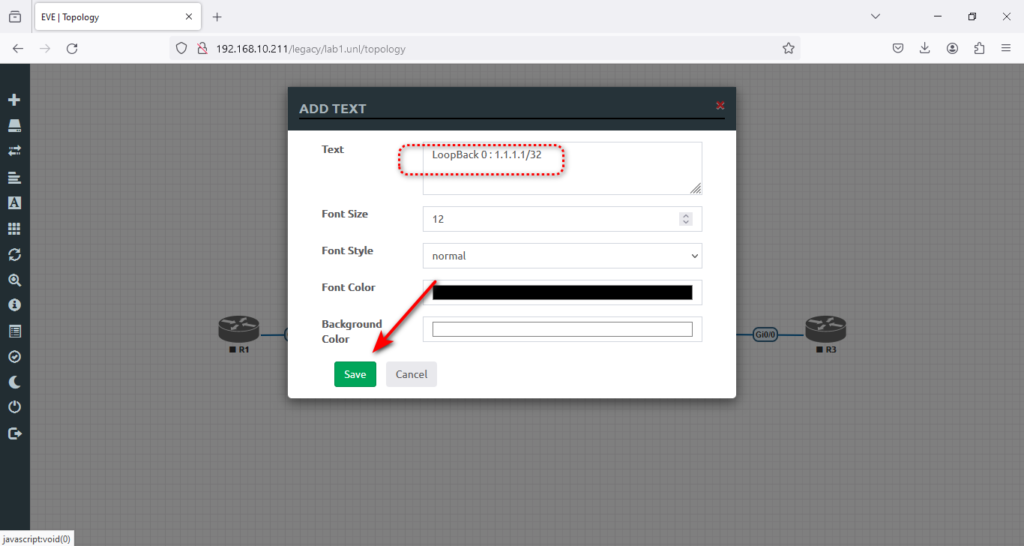
7. Now, we need text notes to understand the topology much better. This will help you focus while practicing in the lab. To do that, click and select text at the top of the R1. Then type LoopBack 0: 1.1.1.1/32 and hit → Save.
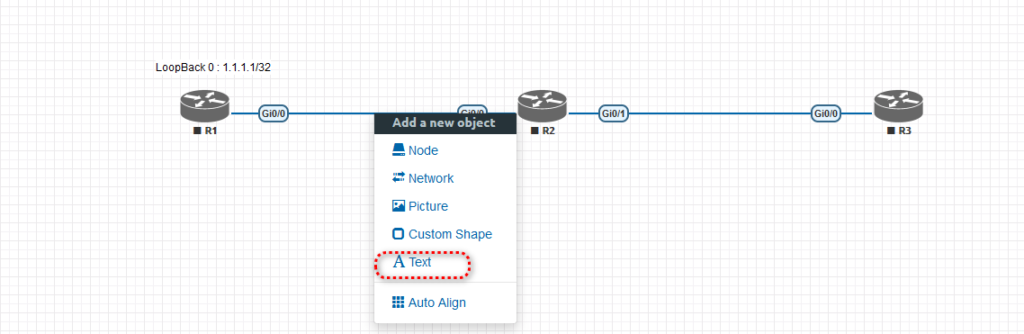
8. We need to add the IP range between routers R1 and R2 and then between R2 and R3. Again, we must right-click the area between R1 and R2 to add a text note.
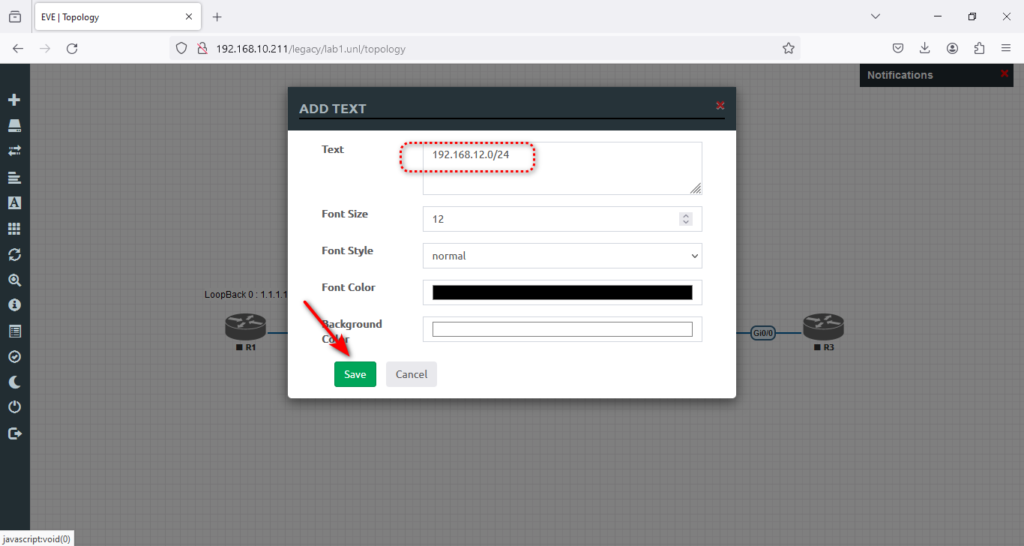
9. You may need to set the text position in the middle of two routers, R1 and R2.
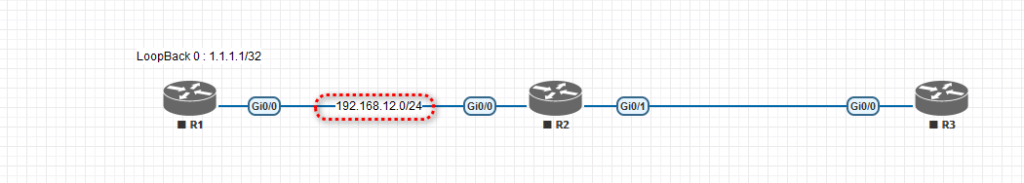
10. So now I need you to add the rest of the text, like the screenshot below, to finish the lab creation.
Great job. Now, here are the lab details.
NOTE — The Ultimate Free EVE-NG Course – Master network simulation with our step-by-step guide and elevate your skills from beginner to pro. Start your free course now!
Step 5. How to Configure Static Routing on a Cisco Router
Static route configuration is a fundamental skill. There are several methods to configure static routes on a Cisco router, each with pros and cons. As a Cisco engineer and in the Cisco CCNA exam, you will be expected to know how to configure static routes via any of the methods available in Cisco IOS.
Lab Objective
This lab exercise aims to configure static routes via Ethernet interfaces between 3 routers. This lab also validates the configured static routes.
LAB: Static Route v1.0
Level: CCNA / Basic
Approximate time: 20 minutes
Preferred image: vios-adventerprisek9-m.SPA.159-3.M6
This LAB will cover topics of
Chapter 16: Configuring IPv4 Addresses and Static Routes
For more information, we suggest “CCNA 200-301, Volume 1 Official Cert Guide.”
Commands Guide:
All commands in this document have this style:
# Interface gig 0/0
If any option specified with italic letters means that you must replace the keyword with a desired value, for example:
# ip address ip_address subnet_mask
# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
And finally, if we mention something in {}, it means that you must use one of the options
# Show ip route| Router | LoopBack 0 | Gi 0/0 | Gi 0/1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1.1.1.1/32 | 192.168.12.1/24 | – |
| R2 | 2.2.2.2/32 | 192.168.12.2/24 | 192.168.23.2/24 |
| R3 | 3.3.3.3/32 | 192.168.23.3/24 | – |
In order to access the router in our lab, we need to install the Windows integration Client pack on our Windows system. Otherwise, we won’t be able to console any nodes in the lab. Below is how to download and initiate the installation.
You should see the downloaded file like this, and you need to double-click and install it.
Tip — You need to accept all the prerequisite files during installation. The wizard will install Putty, VNC client, and Wireshark, and you must take all of that as they are prerequisites and mandatory and must be installed on your system. Below, you can see step-by-step instructions. What I need is to install it like the screenshots below.
Great Job. Now is the time to click on the left menu, select → More actions,
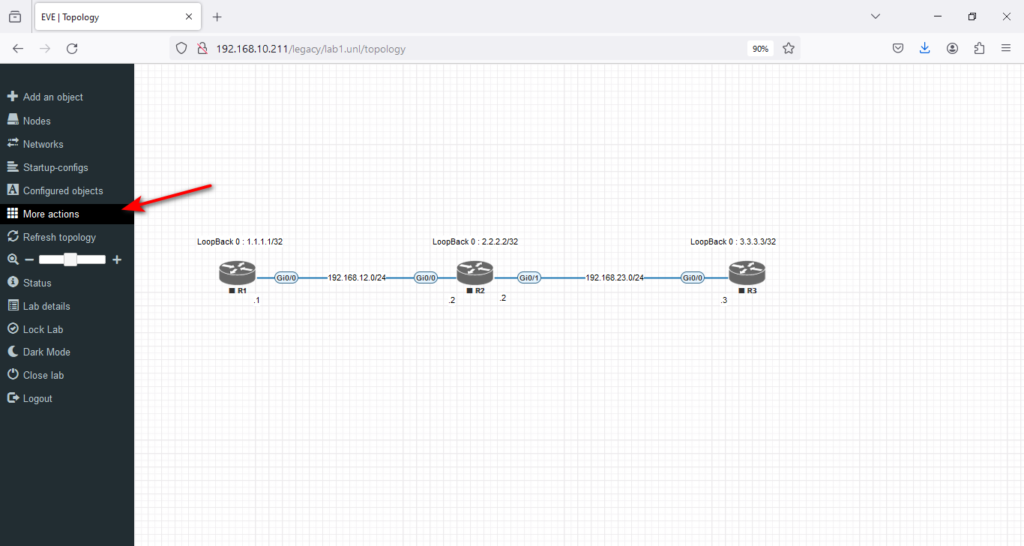
and → Start all nodes.
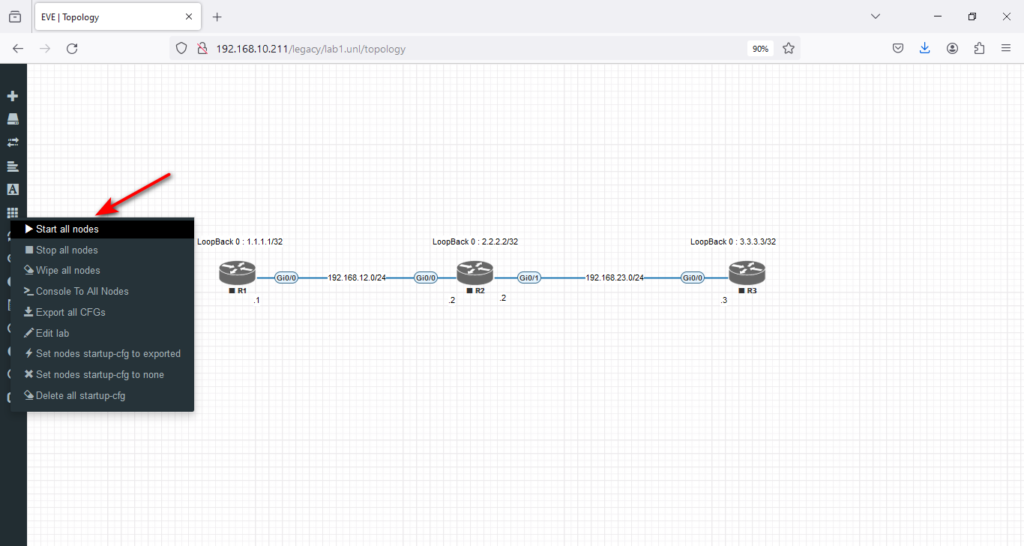
Now is the time to start the lab configuration. I have added tasks, an IP table, and step-by-step instructions (workbook) to help you understand how to start from scratch and finish your lab successfully.
Task 1
Configure the hostnames on routers R1, R2, and R3, as the topology illustrates. Assign addresses as mentioned in Table 1.
| Router | LoopBack 0 | Gi 0/0 | Gi 0/1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1.1.1.1/32 | 192.168.12.1/24 | – |
| R2 | 2.2.2.2/32 | 192.168.12.2/24 | 192.168.23.2/24 |
| R3 | 3.3.3.3/32 | 192.168.23.3/24 | – |
Go to R1, double on the router, and set the basic configuration as instructed.
Router>en
Router#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#interface gig 0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shut
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface loopback 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
R1(config-if)#end
R1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.12.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback0 1.1.1.1 YES manual up up
R1#Go to R2 and set the basic configuration as this instruction
Router>en
Router#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#interface gi 0/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shut
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface loopback 0
R2(config-if)#ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
R2(config-if)#no shut
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface gi 0/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shut
R2(config)#end
R2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.12.2 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.23.2 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback0 2.2.2.2 YES manual up upGo to R3 and set the basic configuration as this instruction
Router>en
Router#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname R3
R3(config)#interface gi 0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shut
R3(config-if)#
*Sep 26 13:57:39.161: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
*Sep 26 13:57:40.162: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface loopback 0
R3(config-if)#ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
R3(config-if)#no shut
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#exit
R3#
*Sep 26 13:58:15.458: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R3#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.23.3 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback0 3.3.3.3 YES manual up up
R3#Task 2
Configure static routes on routers.
R1 Configuration: Due to the diagram, R1 needs to reach 2.2.2.2/32 and 3.3.3.3/32 and 192.168.23.0/24 networks; all these networks are reachable via R2. So, we have to configure 3 static routes for R1 to make this possible. Maybe you guessed we can do that by adding one default route to R2 in this example. For now, we prefer to define 3 separate routes. Look at the example:
R1>en
R1#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.23.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.2
R1(config)#ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.2
R1(config)#ip route 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.2
R1(config)#With these commands, R1 can reach, for example, R3, but R3 has no idea where it is, for instance, 1.1.1.1/32 and how it can reach it. So, we need to configure R2 and R3, too.
Go to the R2 router, and for the first step, check the routing table. As you can see, R2 has two connected routes for 192.168.12.0/24 and 192.168.23.0/24. So, we need to configure two routes for 1.1.1.1/32 and 3.3.3.3/32
R2>en
R2 #show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 2.2.2.2 is directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.12.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.23.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R2(config)#ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.1
R2(config)#ip route 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 192.168.23.3
R2(config)#
The R3 configuration is almost the same as the R1. We need 3 routes for 1.1.1.1/32, 2.2.2.2/32, and 192.168.12.0/24. But this time, let’s use a default gateway instead!
R3>en
R3#conf ter
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.23.2
R3(config)#exitTask 3
After completing our configuration, let’s check it with → ping and → traceroute commands.
We did the test from R3, but you can do the same thing from the others.
R3#ping 1.1.1.1 source 3.3.3.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 3.3.3.3
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/5/7 ms
R3#traceroute 1.1.1.1 source 3.3.3.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 1.1.1.1
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.23.2 3 msec 3 msec 3 msec
2 192.168.12.1 8 msec 12 msec *
R3#
Wrapping Up Your EVE-NG Journey
We’ve come a long way in installing EVE-NG from scratch, designed to suit your needs as a beginner. During this journey, you learned what EVE-NG is, what each of its versions does, and what the minimum system requirements are. It has been an enlightening experience, and I am excited to share my newfound knowledge with you. With EVE-NG, you can create virtual labs and practice networking concepts in a virtual environment. So, EVE-NG can be a great choice if you’re a beginner looking for a platform to experiment and learn.
Where to Go From Here
Now that you’ve successfully installed EVE-NG, it’s crucial to understand that the process doesn’t end here. To truly succeed in network technologies and excel in Cisco exams, it’s essential to dedicate yourself to practice and perseverance. Merely installing the software is just the first step towards accomplishing your goals. Through continuous learning, practical application, and determination, you can effectively answer these exams and successfully execute the required tasks. So, keep pushing forward and never lose sight of your ambitions.
We recommend opting for the EVE-NG LABs Full Pack images to take your journey forward. With this package, you can access a comprehensive collection of 300 scenarios & labs accompanied by clear step-by-step instructions (workbook). You will also have access to 61 useful images that can be effortlessly installed. This Full Pack package will give you invaluable resources to enhance your experience and further excel in your endeavors.
Good luck!

4 responses
på grund af denne vidunderlige læsning !!! Jeg kunne bestemt virkelig godt lide hver eneste lille smule af det, og jeg
I was looking for community version EVE-NG file. I did each step of the instructions to get it. But I haven’t received in my email yet. I hope this site is not fake ?
Thank you for reaching out and sharing your concern. I sincerely apologize for the inconvenience you’ve experienced.
Please rest assured that our site is legitimate, and we’re committed to ensuring you receive what you’ve requested. Sometimes, emails may get delayed or filtered into the spam/junk folder. Could you please double-check those folders in your email?
If you still haven’t received the file, let us know, and we’ll be happy to assist you further or resend the file directly.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!!
Finally I have found something that helped me.
Thank you!