In this lab, we will diagnose and troubleshoot common OSPF issues, including neighbor adjacency failures, missing routes, and LSDB inconsistencies. We will analyze OSPF logs and use debugging tools to resolve problems.
Scenario Description
A company is experiencing intermittent OSPF issues where some routers fail to form adjacencies or routes do not propagate correctly. The administrator must identify and fix the misconfigurations preventing stable OSPF operation.
Since this is a troubleshooting lab, it is better to practice with the save-config LAB.
Network Structure
- Device 1: Cisco Router (R1 – OSPF Router – 192.168.10.1)
- Device 2: Cisco Router (R2 – OSPF Router – 192.168.20.1)
- Device 3: Cisco Router (R3 – OSPF Router – 192.168.30.1)
Topology Diagram
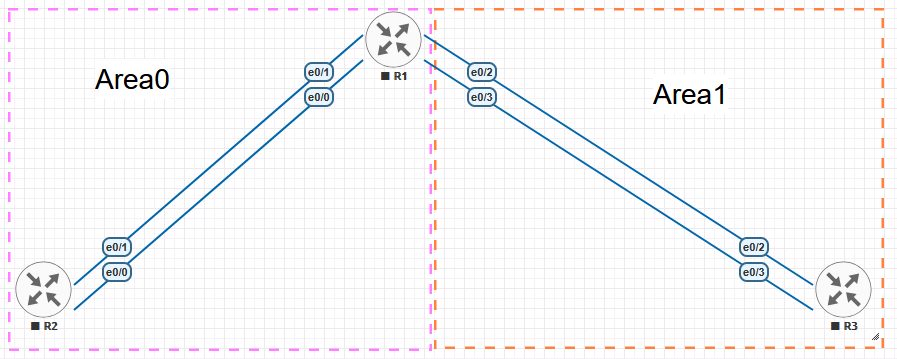
Prerequisites
- Understanding of OSPF neighbor states, LSAs, and routing tables
- Access to Cisco routers
- CLI familiarity
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Checking OSPF Neighbor Adjacencies
Verify if OSPF neighbors have formed properly.
R1#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
2.2.2.2 1 EXSTART/DR 00:00:35 10.1.0.2 Ethernet0/1
2.2.2.2 1 EXSTART/DR 00:00:35 10.0.0.2 Ethernet0/0
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:38 10.3.0.2 Ethernet0/3
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:35 10.2.0.2 Ethernet0/2Why This Step? Ensures that routers are correctly establishing OSPF adjacencies.
Step 2: Diagnosing Missing OSPF Routes
Check if OSPF-learned routes appear in the routing table.
R1#show ip route ospf
192.168.20.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.20.1 [110/11] via 10.1.0.2, 00:00:53, Ethernet0/1
[110/11] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:54, Ethernet0/0
192.168.30.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.30.1 [110/11] via 10.3.0.2, 00:00:58, Ethernet0/3
[110/11] via 10.2.0.2, 00:00:58, Ethernet0/2
1 FULL/DR 00:00:35 10.2.0.2 Ethernet0/2Why This Step? Confirms whether OSPF is successfully advertising and installing routes.
Step 3: Debugging OSPF Adjacency Issues
If neighbor relationships are not forming, enable debugging.
R1# debug ip ospf adjWhy This Step? Helps detect Hello timer mismatches, area mismatches, or subnet mask issues.
Step 4: Checking OSPF Hello and Dead Timers
Ensure the timers match across routers.
R1#show ip ospf interface ethernet0/1
Ethernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.0.1/30, Interface ID 3, Area 0
Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 10
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 10 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 2.2.2.2, Interface address 10.1.0.2
Backup Designated router (ID) 1.1.1.1, Interface address 10.1.0.1
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:08
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Can be protected by per-prefix Loop-Free FastReroute
Can be used for per-prefix Loop-Free FastReroute repair paths
Not Protected by per-prefix TI-LFA
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 2.2.2.2 (Designated Router)
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)If mismatched, adjust the timers:
R1(config)# interface ethernet0/1
R1(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 10
R1(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 40
R1(config-if)# exitWhy This Step? OSPF requires matching Hello and Dead intervals to form adjacencies.