In this lab, we will troubleshoot issues related to default routes and incorrect gateway configurations. We will identify routing problems that prevent external connectivity and fix incorrect default routes.
Scenario Description
A company’s IT team is receiving reports that internal devices cannot reach the internet. The administrator must investigate default route settings, check if the default gateway is properly assigned, and test connectivity after fixing the routing issues.
Since this is a troubleshooting lab, it is better to practice with the save-config LAB.
Network Structure
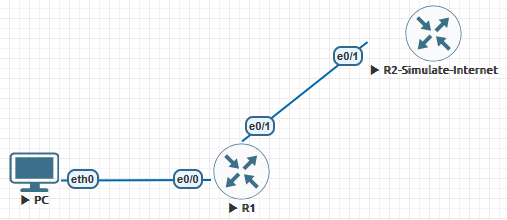
- Device 1: Windows Workstation (Client A – 192.168.10.10)
- Device 2: Cisco Router (R1 – Default Gateway – 192.168.10.1)
- Device 3: Cisco Router (R2 – Internet Gateway – 203.0.113.1 with Simulate 8.8.8.8 – Public DNS)
Topology Diagram
Prerequisites
- Understanding of default routes, next-hop addresses, and static/dynamic routing
- Access to Windows, Linux, and Cisco devices
- CLI familiarity
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Checking the Default Route on R1
R1#show ip route | include 0.0.0.0
Gateway of last resort is 203.0.113.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 203.0.113.1Expected Output:
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 203.0.113.1Fix: If no default route exists, add it:
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 203.0.113.1Step 2: Checking Default Gateway on PC
PC> show ip
NAME : PC[1]
IP/MASK : 192.168.10.10/24
GATEWAY : 192.168.10.1
DNS :
MAC : 00:50:79:66:68:03
LPORT : 20000
RHOST:PORT : 127.0.0.1:30000
MTU : 1500Expected Output:
Default Gateway: 192.168.10.1Fix: If the default gateway is missing, manually configure:
Step 3: Checking Default Gateway on (Linux and Windows – optional)
- On Linux OS
ip route show | grep default- On Windows OS
ipconfig/allExpected Output:
- On Linux OS:
linux-os@root:~$ ip route show | grep default
default via 192.168.153.2 dev ens33 proto dhcp src 192.168.153.128 metric 100- On Windows OS:
Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : TP-Link Wireless USB Adapter
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : B4-B0-24-D3-EF-7D
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::2f46:d16d:a8e3:313c%4(Preferred)
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.65(Preferred)
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . : Tuesday, June 24, 2025 2:58:21 AM
Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . : Wednesday, June 25, 2025 2:58:21 AM
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1Fix: If no default route exists, add it:
- On Linux OS:
sudo ip route add default via 192.168.10.1